Table of contents
Hey 🖐, this is the blog on Web 3.0. In this blog, I will explain what is Web 3.0, decentralization, dApps and many more. So let's start reading the blog.
Introduction
The internet has evolved significantly since its inception, transforming the way we communicate, conduct business, and access information. With each iteration, the web has become more interactive and interconnected. Now, we stand on the brink of a new era known as Web 3.0, promising to revolutionize the internet landscape once again. In this blog, we will delve into the concept of Web 3.0, exploring its key features, potential applications, and the impact it could have on various industries.
What is Web 3.0?
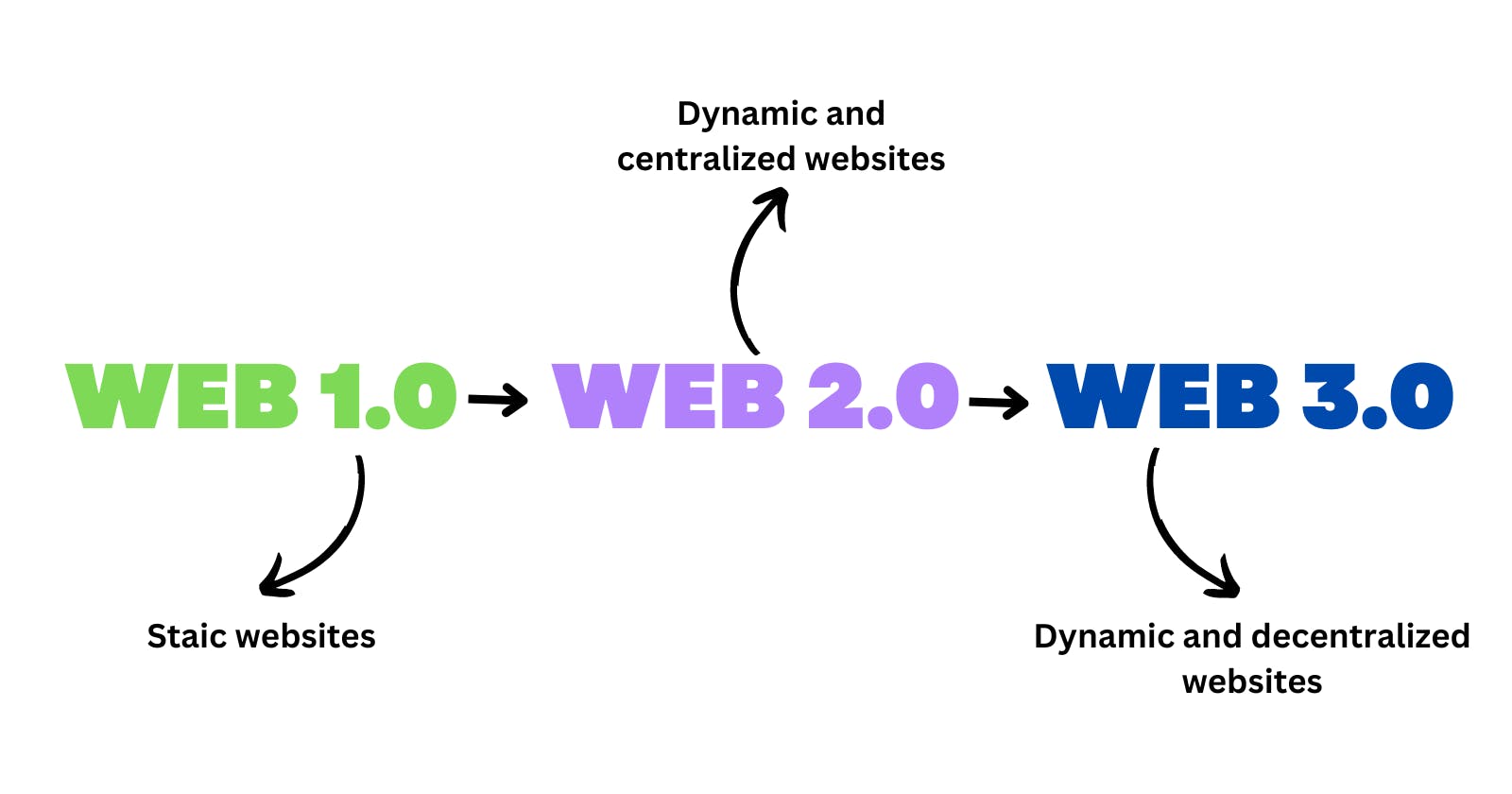
Web 3.0, often referred to as the decentralized web or the semantic web, represents a paradigm shift in the way we perceive and interact with the internet. Unlike its predecessor, Web 2.0, which primarily focused on user-generated content and social media, Web 3.0 aims to create a more intelligent, secure, and decentralized web ecosystem. It leverages emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and decentralized networks to enhance user experiences and empower individuals in unprecedented ways.
Key Features of Web 3.0:
Decentralization: One of the defining features of Web 3.0 is decentralization, where power and control are distributed among participants rather than centralized authorities. Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in enabling decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and secure peer-to-peer transactions.
Enhanced Interoperability: Web 3.0 focuses on enabling seamless interoperability between different platforms, systems, and applications. This allows for the exchange of data and services across various domains, creating a more connected and cohesive digital environment.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Web 3.0 harnesses the power of AI and machine learning algorithms to extract meaning from vast amounts of unstructured data. This enables personalized experiences, predictive analytics, and smarter decision-making.
Semantic Web: Web 3.0 emphasizes the semantic web, which aims to make data more meaningful and understandable to machines. By assigning metadata and context to information, machines can interpret and process data more efficiently, leading to better search results and automated services.
Potential Applications of Web 3.0:
Finance and Cryptocurrencies: Web 3.0 has the potential to disrupt the traditional financial sector by enabling decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, tokenization of assets, and secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries.
Internet of Things (IoT): Web 3.0 can facilitate a more interconnected IoT ecosystem, where devices communicate directly with each other, autonomously execute tasks, and share data securely.
Healthcare: Web 3.0 can revolutionize healthcare by enabling secure and interoperable electronic health records, facilitating medical research collaboration, and empowering patients to have more control over their health data.
Supply Chain Management: By leveraging blockchain technology, Web 3.0 can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, reducing fraud, counterfeiting, and inefficiencies.
Content Creation and Intellectual Property: Web 3.0 can provide content creators with improved copyright protection, direct monetization opportunities, and decentralized platforms that empower artists, writers, and musicians.
Decentralization
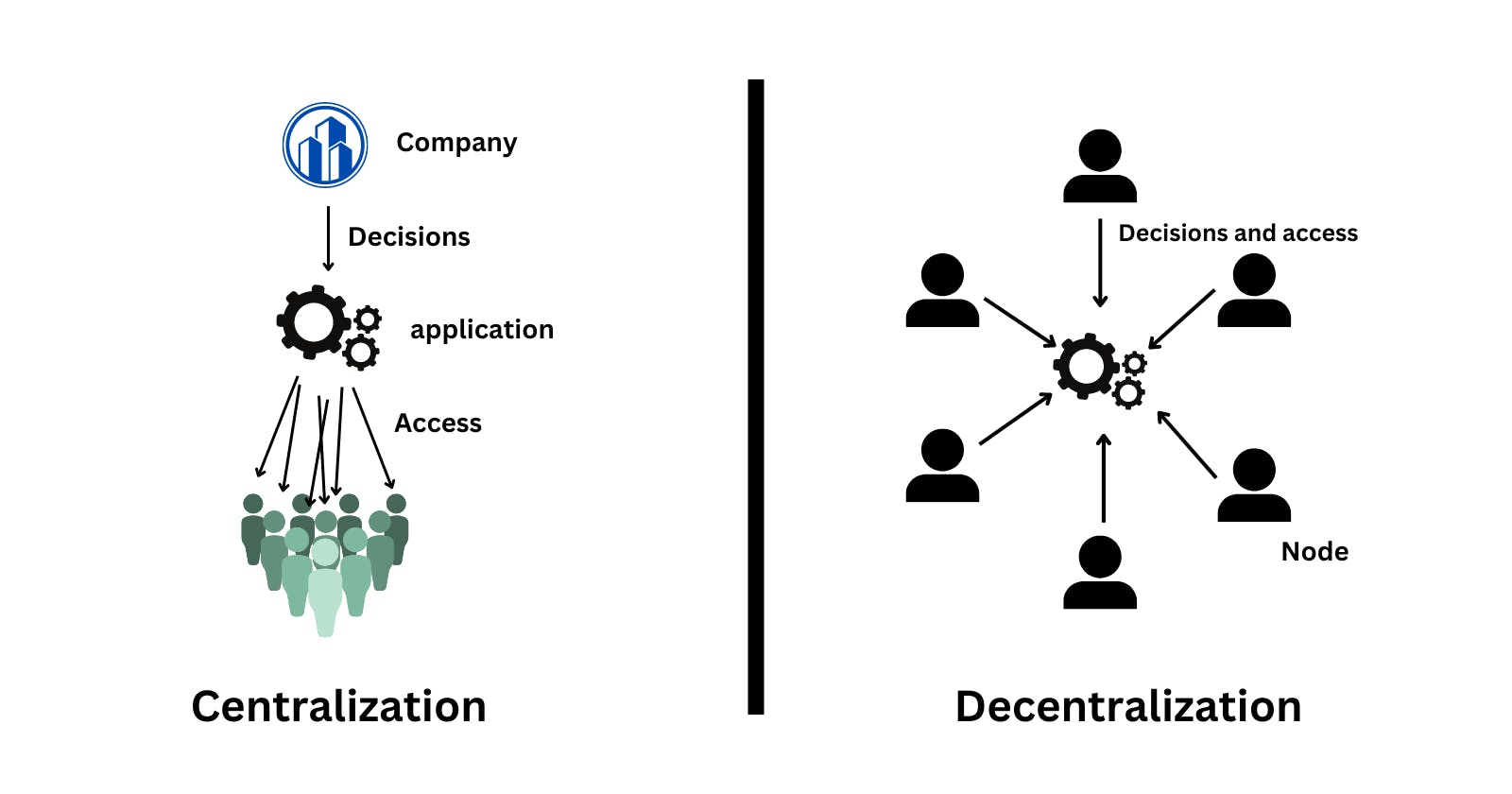
Decentralization refers to the distribution of power, authority, and decision-making across a network or system, rather than concentrating it in a central authority or entity. In a decentralized system, multiple participants have control and influence over the network, ensuring that no single entity holds complete control or can manipulate the system for its benefit.
Decentralization is often associated with emerging technologies like blockchain, which allows for the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) and peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries. Blockchain achieves decentralization by maintaining a distributed ledger that is verified and updated by a network of computers (nodes) instead of a central authority.
The benefits of decentralization are numerous. It fosters transparency, as the shared ledger in a decentralized system is accessible to all participants, reducing the potential for fraud and manipulation. It also enhances security since data is stored across multiple nodes, making it more resistant to hacking or data loss. Decentralization promotes censorship resistance, as it becomes harder for any single entity to control or shut down the system. Furthermore, decentralization empowers individuals by giving them direct control over their data, digital assets, and transactions.
Overall, decentralization represents a shift towards more democratic, transparent, and user-centric systems, offering the potential to disrupt traditional industries and empower individuals in ways not previously possible.
dApps
DApps, short for decentralized applications, are software applications that run on a decentralized network rather than a centralized server. They leverage blockchain technology and smart contracts to enable direct peer-to-peer interactions, removing the need for intermediaries and providing a more transparent and trustless environment.
DApps have found applications in various industries, including finance, supply chain management, gaming, social media, and more. They have the potential to disrupt traditional industries, improve efficiency, and empower individuals by giving them more control over their digital lives.
Some examples of dApps with the replacement of various social media apps we use daily:
Brave Browser: A privacy-focused web browser that rewards users with cryptocurrency for opting into ads and supports decentralized web applications. It is an alternative to Chrome.
DTube: It is a decentralized video platform built on the STEEM blockchain and IPFS peer-to-peer network. It is an alternative to YouTube.
Secretum: It is a decentralized messaging app. It is an alternative to WhatsApp
Audius: It is a decentralized music platform. It is an alternative to Spotify.
Presearch: It is a decentralized search engine. It is an alternative to Google, Yahoo etc.
Conclusion
Web 3.0 represents an exciting vision for the future of the internet. By leveraging emerging technologies, decentralization, and enhanced interoperability, it has the potential to unleash a new wave of innovation and transform various aspects of ours.
Thank you for reading the blog. More on Web 3.0 will be on my upcoming blogs.
Like, Share and Comment. ♥